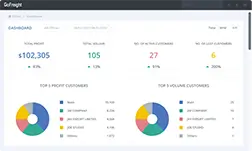
In an ever-competitive world of global trade, mastering freight forwarding comes down to operational efficiency. The landscape, constantly reshaped by advancements from logistics technology companies, necessitates a robust set of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for sustained success. These KPIs serve as a roadmap for evaluating performance, meeting client expectations, and outperforming competitors.
Part I – Core KPIs:
These are the bedrock indicators every freight forwarder needs to implement.
Punctuality in Deliveries: A gauge for the timely arrival of shipments, an essential element for optimizing cost and freight variables.
Customer Contentment Index: A metric indicating the level of customer satisfaction with your freight forwarding offerings.
Documentation Accuracy: Critical in monitoring errors, particularly when it comes to the nuances of cost and freight documentation.
Speed of Incident Settlement: Times the efficiency of solving unexpected problems such as demurrage charges.
Operational Cost-Effectiveness: Reviews how well shipments are managed with regard to cost and freight variables.
Cargo Space Optimization: Focuses on maximizing container utilization, a key factor in avoiding demurrage charges.
Workforce Efficiency: Examines how well workloads are managed in the freight forwarding context.
Regulatory Adherence: Of particular concern considering the complex web of cost and freight regulations, and the risk of accruing demurrage charges.
Record-Keeping Precision: Vital for accurately tracking costs like demurrage charges.
Client Loyalty Metric: Reveals your ability to maintain long-term business relationships in the competitive freight forwarding industry.
Part II – Advanced KPIs:
These delve further into the complexities of operations influenced by innovations from logistics technology companies.
Invoice Timing Accuracy: Ensures prompt billing, crucial in handling any cost and freight-related charges.
Budget vs. Actual Cost Analysis: Studies the precision of your cost and freight forecasts, helping to predict demurrage charges.
Per-Shipment Profitability: Takes into account all associated costs, including any incurred demurrage charges, to give an accurate profit margin.
Partner Reliability Score: Rates the trustworthiness of collaborators, encompassing aspects like demurrage charges and cost and freight.
Optimal Mode of Transport: Evaluates the decision-making prowess in selecting the most cost-efficient and effective transport methods.
Customer Value over Time: Measures the long-term financial benefits each customer brings, including repeat business and referrals.
Resource Usage Efficacy: Monitors the effective utilization of all your freight forwarding resources.
End-to-End Supply Chain Transparency: Critically important for offering real-time updates to clients, a service often bolstered by logistics technology companies.
Exception Management Efficiency: Looks at how well disruptions, such as demurrage charges, are managed.
Tech Integration Index: Measures the adoption rate of technologies, particularly those spearheaded by leading logistics technology companies.
Sustainability Quotient: Keeps track of environmental impacts, a consideration becoming increasingly pivotal in modern freight forwarding.
By understanding and employing these KPIs effectively, freight forwarders can gain invaluable insights into their operations, thereby driving success and sustainability in this dynamic industry.